Apply your code review preferences
CodeRabbit utilizes an internal knowledge base that integrates with several external services to provide a seamless review and issue management experience.
Issue Tracking Integration
CodeRabbit can integrate with your issue tracking systems to provide better context during code reviews. For details on setting up issue tracking integrations, see our Issue Integrations guide.
Learnings
You can tell the bot to remember things about either specific lines in files, or generally about the entire repository, or even across repositories.
For example, you can add a comment in a PR to chat directly with CodeRabbit. @coderabbitai always remember to enforce camelCase.
Or you can comment directly on some lines of code in the PR. @coderabbitai do not complain about lack of error handling here, it is handled higher up the execution stack.
Watch our video walkthrough on learnings for more information.
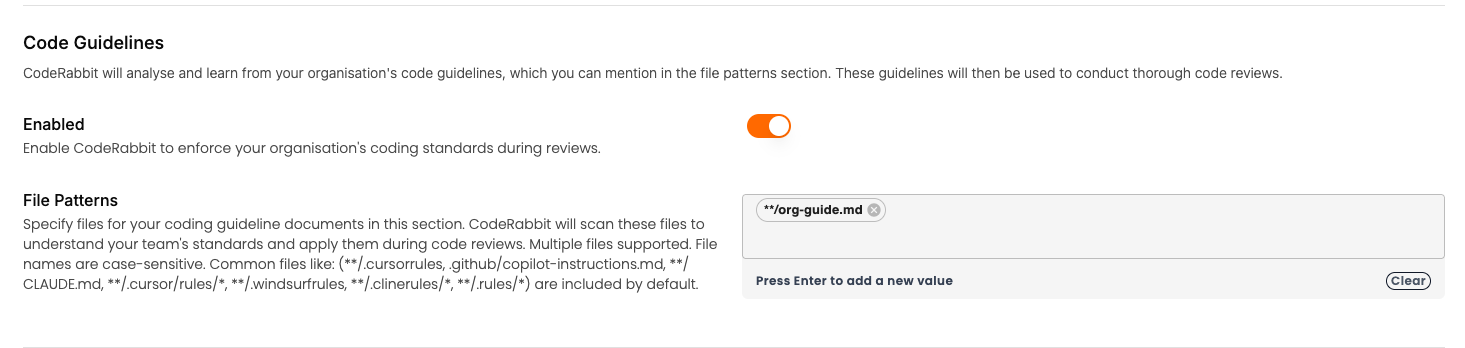
Code Guidelines
CodeRabbit will analyse and learn from your organisation's code guidelines, which you can set up in the knowledge base section. These guidelines will then be used to conduct thorough code reviews.
The following patterns are scanned by default.
**/.cursorrules
.github/copilot-instructions.md
**/CLAUDE.md
**/.cursor/rules/*
**/.windsurfrules
**/.clinerules/*
**/.rules/*